
Poisoning/Diseases Caused by Toxins – Helpline
Poisoning in livestock is quite common. In order to help the veterinarians and the farmers get information on the diagnosis and treatment of poisonings, we are offering this service. We will update the information.
Currently, the helpline is based on type of poison/ toxin but in future we will provide symptom-based helpline.
Nitrate Poisoning
It is a very common plant-associated poisoning. Many forages, weeds are known to cause acute and chronic poisoning.
- Corn
- Millet
- Oat
- Soybean
- Sorghum,
- Sudan Grass
- Sweet Clover
- Wheat
Acute:
Symptoms are shown immediately after eating large amount of nitrate-containing forages. Nitrate content is very high in young forages. The content is very high if the crop is harvested and with rains new shoots crop-up and cattle are left to graze.
- Bluish/chocolate brown mucous membranes
- Rapid/difficult breathing
- Noisy breathing
- Rapid pulse (150+/minute)
- Salivation, bloat, tremors, staggering
- Weakness, coma, death
- Dark “chocolate-coloured” blood
- Pregnant females that survive nitrate poisoning may abort due to a lack of oxygen to the fetus.
- Abortions generally occur approximately 10 to 14 days following exposure to nitrates.
Chronic:
- Reduced reproductive efficiency in adult cattle
- Lower weight gains with or without decreased feed intake in young stock.
- Research has shown that serum progesterone concentrations may be decreased greatly in open animals (50%) more moderately in early pregnancy (25%), and very little, if any, in mid- or later pregnancy.
- Services per conception and first service conception rates may be most noticeably affected, resulting in more repeat breeding
- Check fodder / forages for nitrate content / blood for methaemoglobin
Diagnosis:
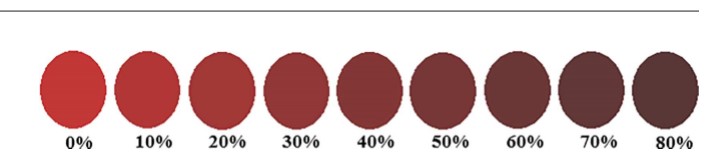
Field tests are available. It is quite easy to diagnose nitrate poisoning from the colour of the blood.
Take a white absorbent filter paper disc and put a drop of fresh blood on it. Compare it with the chart provided herein. (Give the chart here to compare)
 |
 |
Treatment:
- Methylene blue Injection, (1% ) 1 to 2 ml per kg body weight to be given i.v. slowly
- (Pravon Blue- Avalon Pharma, Mumbai and Flagship Biotech International Pvt. Ltd. Thane).
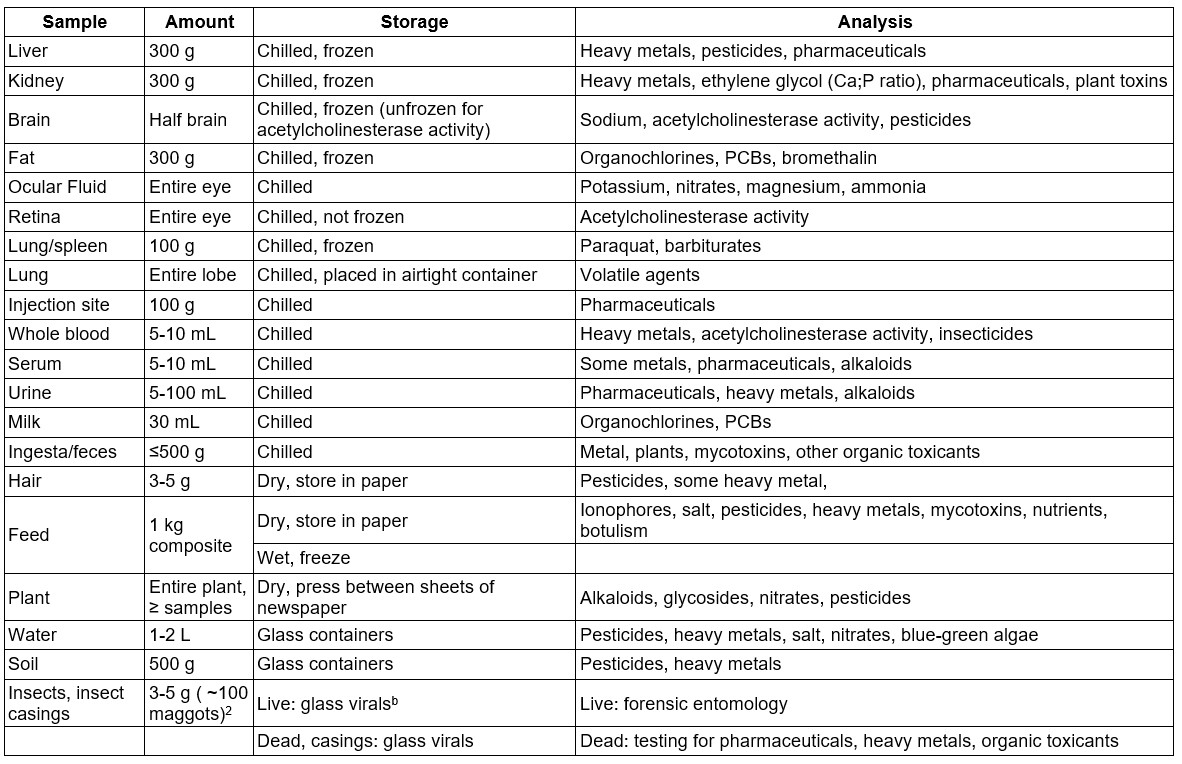
Sample Collection for Toxicology
Read: General Approach to Treating Poisoning and Toxin-associated Diseases in Cattle
